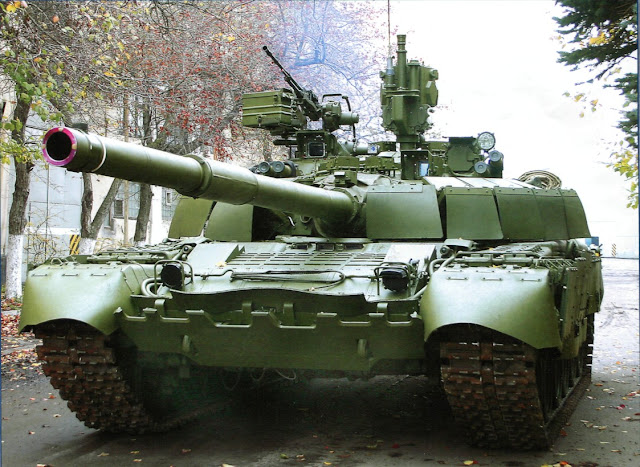
GTD-1000 - GTD-1000TF - GTD-1250 Gas Turbine Engines
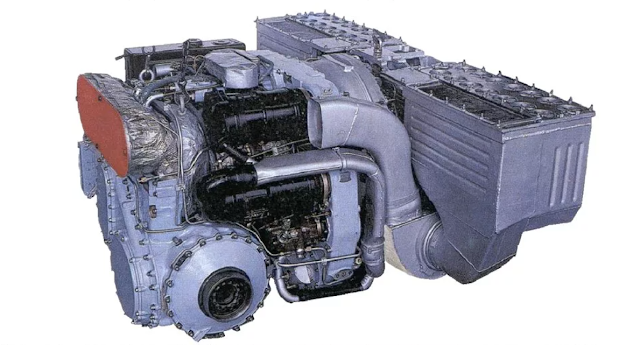
The world's first mass-produced tank gas turbine engine GTD-1000T was created at the Klimov Plant in 1968 for the T-80 main battle tank developed By the special tank design Bureau of the Kirov plant (now JSC "Spetsmash"), which was adopted by the Soviet Army in 1976. Since 1980, a modification of the GTD‑1000TF for T-80B/BV tanks was produced, since 1986 a modification of the GTD-1250 for T-80U tanks. GTD-1250 Engines of the GTD-1250 family as part of the power plants of T-80 tanks are in service with the armies of Russia, Belarus, Cyprus, South Korea, Kazakhstan. Turbine engine GTD-1000T/GTD-1250, which have a large volume-weight capacity and a more favourable traction characteristic compared to diesel engines, provide T-80 tanks with interesting characteristics: - higher operational readiness - easy start-up at low temperatures (up to -40°C) - better cross-country ability on soils with a low load-bearing capacity - best noise and heat-masking qualities - increased ...








