T-54/T-55 with GTD-3T gas turbine engine
In the early 1960s, an R&D program was launched to create a promising next-generation tank. T-54 and T-55 tanks were the basis for various running models, designed to test new components and systems. The GTD-3T gas turbine engine and its supporting systems, the hydromechanical transmission, the placement of the driver in the turret, automated control drives, and the chassis of new experimental tanks were tested on these models.
 |
| T-54 with GTD-3T |
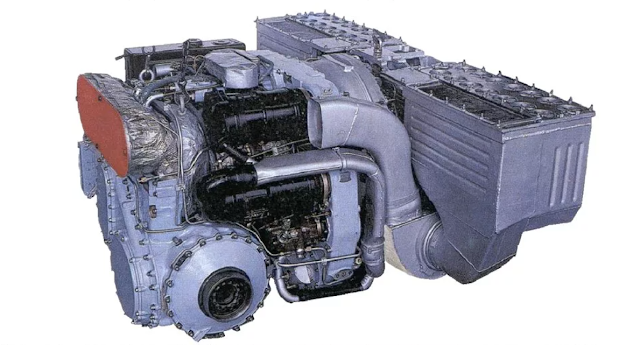
Between 1960-1961 Factory No.174 (Zavod No.174) and VNII-100 created a mobility trial mockup using a T-54 and fitted it with a GTD-3T gas turbine engine which unregulated produced 515kW (700 hp), during the installation process the turbine engine's performance was reduced to 318kW (432 hp).
Compared to the baseline T-54, the new variant mainly had its engine transmission bay changed. The GTD-3T displaced more inner volume compared to the standard V-54 diesel engine. Larger volume displacement meant that the engine was 140 mm closer to the separating plate between the crew compartment and engine bay. Such placement resulted in the exhaust being blocked by the turret. To install a new exhaust vent, which was facing 30° upwards and towards the rear, several fuel tanks had to be removed. To remove combusted gases, an exhaust tube facing 45° upwards was used.

 |
| GTD-3T cross-section view. |
The engine starting procedure was carried out with the help of an ST-1PT electric starter. In cold climates (-22C) the average time to spool up the turbine would be around 7 minutes.
To operate the engine, the original analog indicator panel was adapted for the use of a GTD-3T.
For providing onboard power, an aviation-type generator (GSK-1500) was coupled with the transmission.
 |
| T-55 with GTD-3T at VNII-100 testing facility in 1964. |
During 1963-1964, VNII-100 carried out further GTD-3T trials utilizing a T-55 as the mobility trial mockup. This variant utilized the maximum engine performance of 515kW (700hp). The T-55 mockup utilized 2 different transmissions: a standard mechanical transmission taken from the baseline vehicle and a prototype GMT-150 hydromechanical transmission.
Cross-section of the GMT-150 hydromechanical transmission
Throughout the 4 years of development, 4 different variants were created, refining the onboard systems and implementing the engine on 2 different vehicles.
Taken from: Павлов М. В., Павлов И. В. Отечественные бронированные машины 1945-1965 гг. Часть I. Легкие, средние и тяжелые танки.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------





Comments
Post a Comment